
Solving Gaussian Integral (integration of gaussian function) using Feynman’s Method. YouTube
Kasper Müller · Follow Published in Cantor's Paradise · 10 min read · Jan 18, 2022 -- 7 Richard Feynman in 1959. Picture is from Wikimedia Commons. Differentiation and integration are two sides of the same coin. Sometimes we call that "coin" calculus.

∫sin(√3 ln(x))/ln(x) [0, 1]. Solving challenging integration problem using Feynman’s Integral
2 Answers Sorted by: 1 If your heart's set on a solution using Feynman's trick, note ∫∞ 0re − ar2dr = 1 2a ∫∞ 0r3e − ar2dr = 1 2a2. So − I(a)I′(a) = ∫R2x2e − ar2dxdy = ∫2π 0 cos2θdθ∫∞ 0r3e − ar2dr = π 2a2.
Solving the Gaussian Integral using the Feynman Integration method by Rthvik Raviprakash Medium
On its last page, the author, Mr. Anonymous, left several exercises without any hints, one of them is to evaluate the Gaussian integral ∫∞ 0 e−x2 dx = π−−√ 2 ∫ 0 ∞ e − x 2 d x = π 2 using this parametrization trick. I had been evaluating it through trial and error using different paramatrizations, but no luck so far.
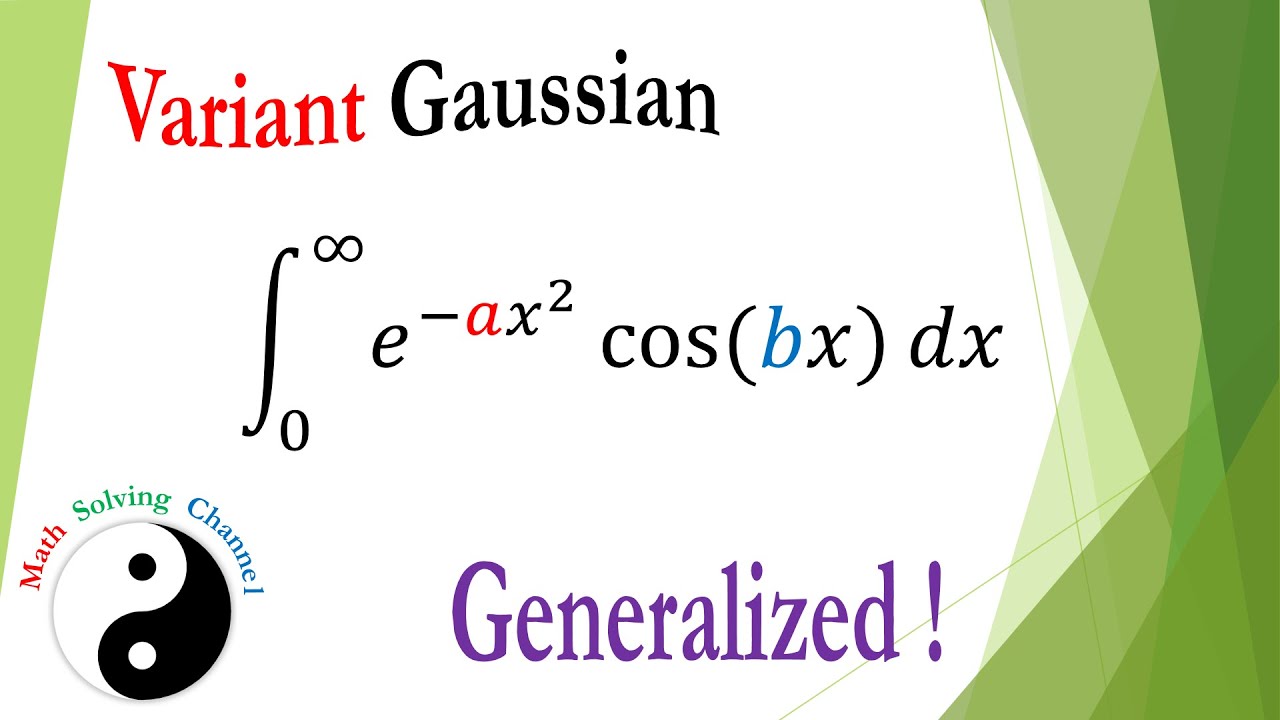
Variant Gaussian Integral e^(a x^2)cos(b x), from 0 to infinity, General Case, Feynman's trick
Inactive can be used to derive identities by applying standard techniques such as Feynman's trick of differentiating under the integral sign. Derive a closed form for by analyzing . In [1]:=. Out [1]=. First differentiating with respect to at produces the desired integral. In [2]:=.

Integrate with Feynman's trick and Gaussian Integral YouTube
1. DERIVATION OF THE GAMMA FUNCTION An old problem is to extend the factorial function to non-integer arguments. This was resolved by Euler, who discovered two formulas for n! (one an integral, the other an infinite product) which make sense even when n is not an integer.

∫e⁻²ˣ²cos(3x) dx [∞,∞]. Solving Integration by Feynman’s Trick with extension of Gaussian
Feynman's Favorite Trick 3.1 Leibniz's Formula The starting point for Feynman's trick of 'differentiating under the integral sign,' mentioned at the end of Chap. 1, is Leibniz's formula. If we have the integral IðÞ¼α ð bðÞα aðÞα fxðÞ;α dx where α is the so-called parameter of the integral (not the dummy variable of

The Feynman integration trick and Leibniz rule epitomized with three examples YouTube
POWERFUL Integration Technique!! - Feynman's Trick: Ideas and Examples | Gaussian Integral Math&Others 5.74K subscribers Subscribe 39 1.5K views 10 months ago Calculus Do you want to learn.

Feynman’s integral tricks for solving challenging integration problem. YouTube
However, as we will see, utilizing Feynman's path-integral formulation of quantum mechanics, Gaussian integrals are also central for computation in quantum statistical mechanics and more generally in quantum field theory. A. one degree of freedom Let us start out slowly with standard, scalar, one-dimension Gaussian integrals Z 0(a) = Z ∞.

Visual proof of Feynman's Trick Leibniz Integral rule YouTube
Feynman's Favorite Trick 3.1 Leibniz's Formula The starting point for Feynman's trick of 'differentiating under the integral sign,' mentioned at the end of Chap. 1, is Leibniz's formula. If we have the integral IðÞ¼α ð bðÞα aðÞα fx,ðÞα dx where α is the so-called parameter of the integral (not the dummy variable of

Feynman's Technique This is the greatest integration method of All Time YouTube
The trick of inverting Feynman's trick by integrating the integral of interest to make a double integral and then reversing the order of integration is introduced. The Cauchy-Schlӧmilch transformation is stated, derived, and used to evaluate some interesting variations of the probability integral. Download chapter PDF 3.1 Leibniz's Formula

Solving a nice integral via Feynman's trick YouTube
The double integrals are surface integrals over the surface Σ, and the line integral is over the bounding curve ∂Σ. Higher dimensions. The Leibniz integral rule can be extended to multidimensional integrals. In two and three dimensions, this rule is better known from the field of fluid dynamics as the Reynolds transport theorem:

Solve Integral by using Feynman's Trick (Leibniz integral rule) (1e^(x^2))/x^2 from 0 to
Subscribed Share 203 views 4 months ago Feynman's trick of differentiating under the integral sign, also known as Leibniz' rule. In this video we work through a simple proof of the rule, and.

Integral of ln(x) with Feynman's trick! YouTube
Find the Integral x^2e^-x^2 (x squared multiplied by e raised to x square) using a simple,fast and interesting method using Gaussian integral and differentia.

POWERFUL Integration Technique!! Feynman's Trick Ideas and Examples Gaussian Integral YouTube
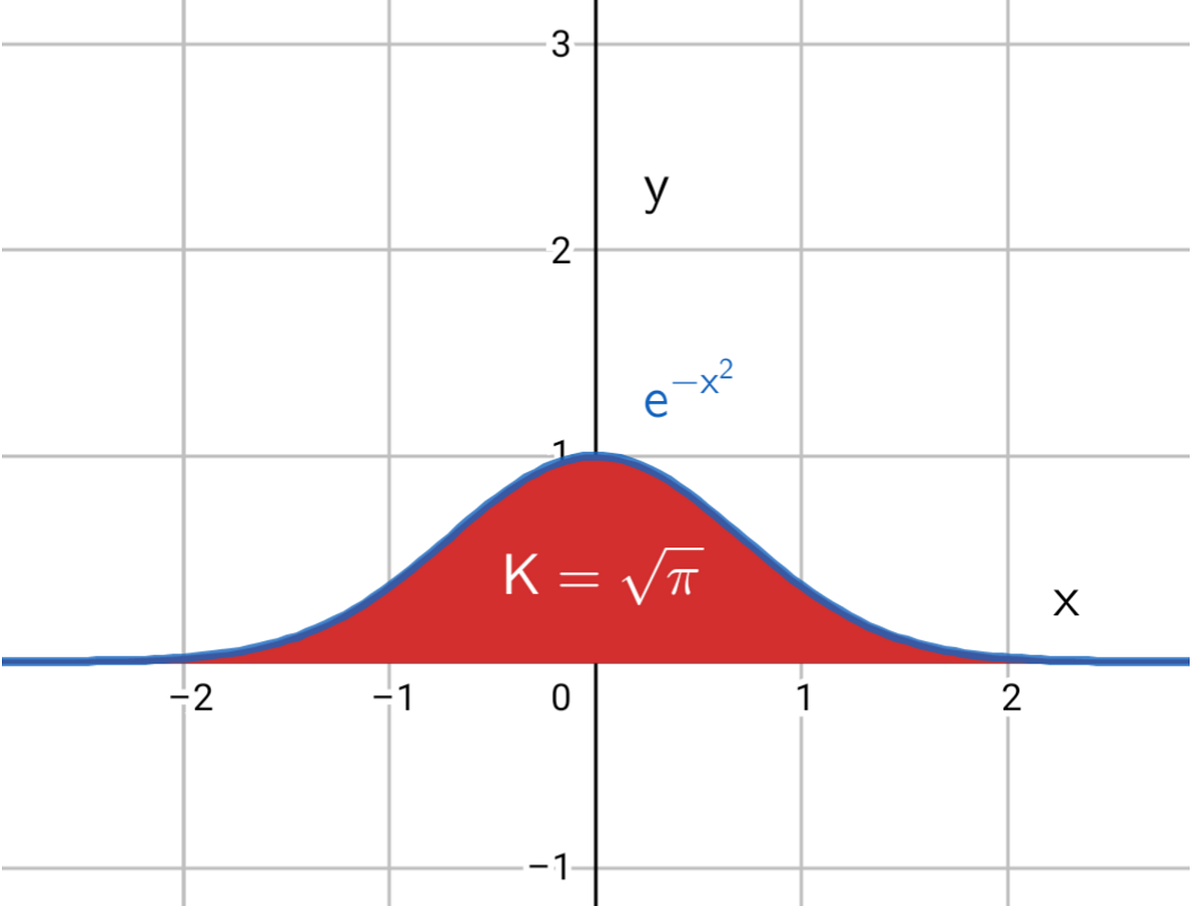
This is known as the Gaussian integral, after its usage in the Gaussian distribution, and it is well known to have no closed form. However, the improper integral. I = \int_0^\infty e^ {- x^2} \, dx I = ∫ 0∞ e−x2 dx. may be evaluated precisely, using an integration trick. In fact, its value is given by the polar integral.

A Crazy Integral (Feynman's Trick) [Difficulty 4] YouTube
Feb 23, 2022 2 Graphical representation of the Gaussian Integral (Image: Wikimedia Commons) The first time I came across the Gaussian integral, also known as the Euler-Poisson integral,.

Lect_1 FEYNMAN PATH INTEGRAL YouTube
Feynman's Trick I: Di erentiating Under the Integral Sign Saavanth Velury September 25, 2020 Throughout this course and later on in your potential physics career, you will always run across having to compute moments of exponential and Gaussian distributions.